Biochemistry Chapter 4 Nucleic Acids
Nucleic Acids in Agriculture
Nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, are essential in modern farming. They help scientists develop better crops, protect plants from diseases, and improve livestock breeds. Let’s explore how they are used in agriculture with real examples that BSA 2 students might encounter.
1. Improving Crops Through Genetic Engineering
DNA and RNA are used to create genetically improved plants that have beneficial traits. Some examples include:
- Pest-Resistant Crops: Scientists have modified corn (Bt corn) to produce a protein that kills harmful pests like corn borers. This reduces the need for chemical pesticides and helps farmers get higher yields.
- Drought-Tolerant Rice: Researchers have developed rice varieties like Sahbhagi Dhan and IR64-Sub1, which use special genes to survive with less water, making them useful in dry areas.
- Disease-Resistant Tomatoes: Some tomato plants are genetically engineered to resist viruses, such as the Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus, which can destroy entire crops.
2. Fighting Plant Diseases
Nucleic acids help detect and control plant diseases early. Farmers and researchers use DNA and RNA-based tests to identify infections before they spread.
- Early Virus Detection in Bananas: Scientists test banana plants for the Banana Bunchy Top Virus (BBTV) using DNA-based techniques, helping prevent outbreaks.
- RNA Interference (RNAi) for Disease Resistance: Papaya varieties like Rainbow and SunUp have been developed to resist the Papaya Ringspot Virus using RNA-based technology.
3. Improving Soil Fertility with Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria
Certain bacteria help plants get nitrogen from the air, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers. DNA helps scientists study and improve these bacteria.
- Legume Crops (Soybeans, Peanuts, Mung Beans): These crops form a partnership with Rhizobium bacteria, which use DNA instructions to fix nitrogen in the soil, making it more fertile.
- Genetically Improved Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria: Scientists are modifying nitrogen-fixing bacteria like Rhizobium and Azospirillum to enhance their efficiency, reducing farmers’ dependence on synthetic fertilizers.
4. DNA in Livestock Improvement
DNA is also used to improve farm animals, making them healthier and more productive.
- Faster-Growing Chickens: Selective breeding programs use DNA testing to choose fast-growing chicken breeds like Broilers (e.g., Cobb 500, Ross 308), which are bred for rapid growth and disease resistance, ensuring a steady meat supply.
- Disease-Resistant Cattle: Scientists use DNA markers to breed cattle breeds like Nelore and Brahman, which are resistant to common diseases like Foot-and-Mouth Disease, reducing losses for farmers.
- Milk Production in Dairy Cows: DNA testing helps identify cows with genes for high milk production, allowing farmers to breed better dairy herds.
5. Nucleic Acids in Grafting
Grafting is a common technique used in fruit trees. Scientists are now using nucleic acids to transfer disease resistance from genetically modified rootstocks to non-modified scions.
- Stronger Mango and Citrus Trees: By grafting resistant rootstocks with desirable scions, farmers can grow trees that are both productive and resistant to soil-borne diseases like Fusarium wilt.
Understanding DNA and RNA
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) store and transmit genetic information in all living things. Here’s a simple guide:
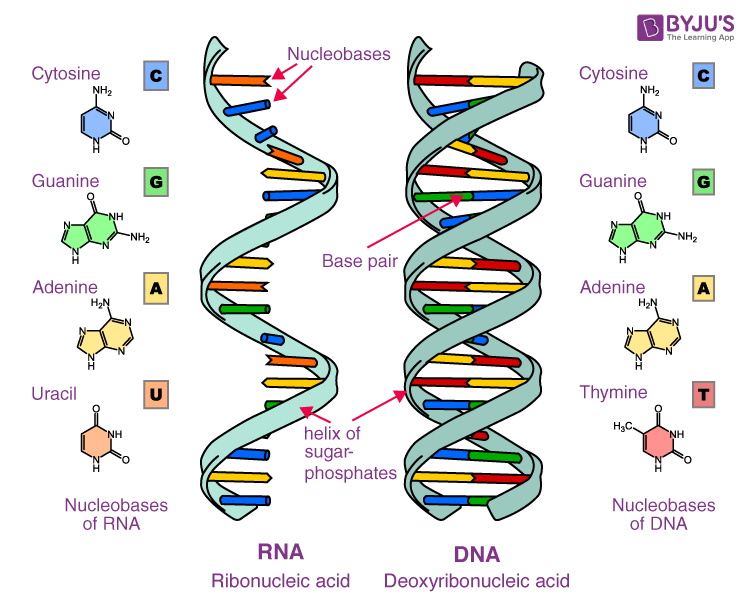
Structure of DNA: The Double Helix
DNA looks like a twisted ladder (double helix). Each step of the ladder is made of nucleotides, which include:
- Sugar (Deoxyribose) – A type of sugar that helps form the backbone.
- Phosphate Group – Connects the sugars to keep the structure strong.
- Nitrogen Bases – The "letters" of the genetic code:
- Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T)
- Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G)
This pairing is like puzzle pieces that always fit together the same way!
Structure of RNA: The Messenger
RNA is like DNA’s helper. Instead of a double helix, RNA is single-stranded and more flexible.
Key Differences from DNA:
- Sugar: RNA has ribose instead of deoxyribose.
- Base Change: Uracil (U) replaces Thymine (T).
- Shape: RNA can fold into different forms to do different jobs.
Roles of DNA and RNA
- DNA stores genetic instructions for plant and animal traits.
- RNA helps make proteins that control growth, disease resistance, and other functions.
- mRNA (Messenger RNA): Carries genetic instructions for making proteins.
- tRNA (Transfer RNA): Helps assemble proteins using amino acids.
- rRNA (Ribosomal RNA): A key part of ribosomes, where proteins are made.
How Nucleic Acids Influence Inheritance and Evolution
- DNA Replication: Ensures genetic information is passed from parents to offspring, whether in plants or animals.
- Mutations and Evolution: Mutations in DNA can lead to new traits, such as drought resistance in crops or better disease resistance in livestock.
- RNA Viruses in Agriculture: Some livestock diseases (like Foot-and-Mouth Disease) are caused by RNA viruses, which evolve quickly. Understanding RNA helps scientists develop better vaccines.
Conclusion
Nucleic acids play a big role in agriculture, from improving crops and livestock to detecting diseases and enhancing soil fertility. By understanding DNA and RNA, future agricultural professionals can use biotechnology to create more sustainable and productive farming systems.
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
Comments
Post a Comment